As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.
Microscopy, the art of exploring the unseen, has been a cornerstone in scientific discovery for centuries. From unravelling the mysteries of cells to unlocking the intricacies of the smallest particles, Our knowledge of the microscopic world has grown significantly thanks in large part to the invention of microscopes. In this digital age, where scientific advancements continue to push boundaries, the choice between different types of microscopes becomes critical. As we delve into the realm of electron microscopes and light microscopes, it becomes essential to grasp their fundamental differences and understand their unique contributions to scientific inquiry. We’ll set out on a quest to understand the subtle differences between electron and light microscopes in this post, shedding light on their individual roles in shaping the landscape of scientific exploration. Join us as we explore how these powerful instruments have revolutionized the way we perceive and analyze the microscopic universe.
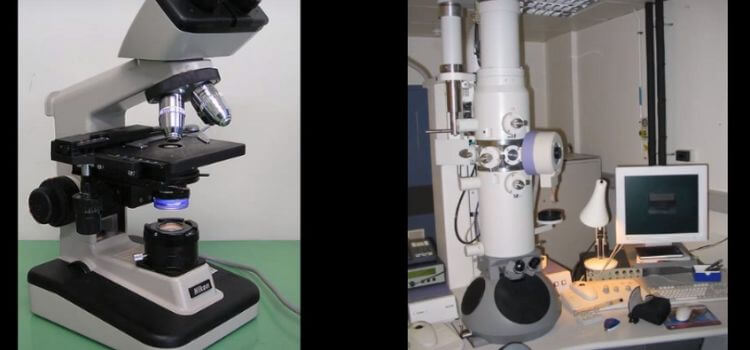
Light Microscopes
We’re turning our attention to the trusty workhorse of the scientific world – the light microscope. You know, the one that’s been a staple in biology labs and classrooms for as long as we can remember. But hey, there’s more to it than meets the eye (pun intended)! Join me as we unravel the secrets behind the functioning, perks, and quirks of these light-based marvels.
How Light Microscopes Work:
1. Use of Visible Light for Illumination:
Picture this: a beam of light shining through a lens, hitting that tiny specimen on the glass slide. That’s how the magic begins. Light microscopes rely on good old visible light to illuminate the microscopic stage, revealing the hidden details of tiny wonders.
2. Magnification and Resolution Capabilities:
Ever marvelled at the intricate details of a butterfly wing or a plant cell? Thank the magnification power of light microscopes! These microscopes can zoom in on specimens, making the small appear large. However, it’s not just about size; resolution matters too. It determines how clear those details appear, and light microscopes do a decent job capturing them.
Limitations of Light Microscopes:
1. Resolution Constraints:
As much as we love our light microscopes, they do have their limitations. Picture it like watching your favorite show on an old TV – you get the idea, but the details might not be as crisp. Light microscopes have a resolution limit, meaning they can only reveal details down to a certain level.
2. Specimen Thickness Limitations:
Here’s the scoop: light struggles with thick specimens. If your sample is too hefty, the light might not penetrate it well, leaving you with a blurry image. So, while these microscopes are fantastic for thin slices, they might not ace the game with thicker samples.
Pros and Cons:
Pros
Cons
Electron Microscopes
we’re diving deep into the microscopic realm with a fascinating topic – electron microscopes. If you’ve ever wondered how scientists uncover the tiniest secrets of our world, you’re in for a treat. Buckle up as we demystify the incredible world of electron microscopy and explore its two rockstars – Scanning electron microscopes and transmission electron microscopes. But let’s review the fundamentals first.
1. Introduction to Electron Microscopy:
Imagine a world where we can zoom in beyond the capabilities of regular microscopes. That’s the magic of electron microscopy! Instead of using visible light, electron microscopes employ electron beams to capture mind-blowingly detailed images. The result? Higher magnification and resolution than your trusty light microscope.
2. Transmission Electron Microscopes (TEM):
Now, let’s meet TEM – the superhero of seeing things on a super-small scale. This microscope works on the principle of transmitting electrons through ultra-thin specimens. It’s like peeking through the microscopic keyhole! TEM goes beyond the limits of light microscopes, revealing the inner structure of cells, tissues, and materials at an unprecedented level. Applications? Oh, they range from unraveling the secrets of nanomaterials to understanding the intricate details of biological cells.
3. Scanning Electron Microscopes (SEM):
Next up, SEM – the rockstar of surface imaging! SEM takes a different approach by scanning the specimen’s surface with focused electron beams. This technique creates stunning 3D-like images, giving us a whole new perspective on the surfaces of objects. From the intricacies of insect wings to the texture of materials, SEM captures the beauty of the microscopic world in exquisite detail.
Pros and Cons :
Pros
Cons
Key Differences Between Electron and Light Microscopes
let’s dive into the fascinating world of microscopes. We all know these magical instruments reveal the hidden details of the tiniest things but have you ever wondered what sets electron microscopes and light microscopes apart? Buckle up, as we unravel the key differences between these powerhouse devices and how they shape our understanding of the microscopic realm.
Understanding the Basics:
First off, let’s get back to Microscopy 101. Light microscopes, the OGs of the microscopic world, use visible light to illuminate specimens, letting us peer into the small wonders of the world. On the other hand, electron microscopes, the tech-savvy siblings, ditch the light for electron beams, taking magnification and resolution to a whole new level.
Magnification Madness:
One major difference that sets these siblings apart is their magnification game. Light microscopes do a fantastic job, magnifying things up to a thousand times. But hold your horses, because electron microscopes blow that out of the water, zooming in to levels a regular microscope can only dream of – think millions of times!
Resolution Revolution:
Resolution, the fine detail you can see in an image, is where electron microscopes flex their muscles. Light microscopes, while awesome, have a resolution limit due to the wavelength of visible light. Electron microscopes, being the overachievers they are, overcome this limit, revealing details finer than a strand of hair.
TEM vs. SEM Showdown:
Now, let’s talk about TEM and SEM – the cool acronyms in the microscopy world. Transmission Electron Microscopes (TEM) let us peek inside specimens, while Scanning Electron Microscopes (SEM) capture stunning 3D images of surfaces. It’s like having two superheroes with unique powers in the same squad!
Wrap-Up and Your Next Adventure:
So, there you have it – the lowdown on the key differences between electron and light microscopes. These tools may seem similar, but each brings its own superhero powers to the microscopic table. Next time you’re gazing through an eyepiece or analyzing jaw-dropping microscopic images, you’ll know the tech behind the magic. Stay curious, stay fascinated, and join us on the next adventure into the extraordinary world of science!
Real-world Applications
we’re diving into the real-world applications of electron and light microscopes, those unsung heroes of scientific exploration. Strap in as we explore the mind-blowing breakthroughs these microscopes have made possible.
Section A: Scientific and Medical Marvels with Electron Microscopes
Ever wondered how scientists peer into the tiniest realms of life? Enter electron microscopes, the wizards of the microscopic world. Thanks to these high-tech marvels, scientists have unraveled the secrets of cell structures, viruses, and even atoms! Imagine being able to see the intricate details of a virus, helping us develop targeted treatments and vaccines. It’s not just about the small stuff, though; electron microscopes have been instrumental in material science, allowing us to engineer materials at the atomic level for groundbreaking innovations.
Section B: Light Microscopes – Illuminating Various Fields
Now, let’s not forget our trusty light microscopes. While electron microscopes take the spotlight for minuscule wonders, light microscopes have made significant contributions too. In biology, they’ve been the go-to tool for studying larger cells and tissues, helping us understand the complex world of living organisms. But their influence doesn’t stop there – light microscopes have been crucial in fields like geology, where they unveil the mysteries of rocks and minerals, and materials science, aiding in the development of new materials for everyday use.
In a nutshell, electron and light microscopes aren’t just gadgets for scientists; they’re portals to hidden worlds that spark innovation and drive scientific progress. As we marvel at the incredible breakthroughs facilitated by these microscopes, it’s clear that their impact extends far beyond the laboratory, touching every aspect of our lives. So, here’s to the tiny heroes who empower us to see the unseen and push the boundaries of knowledge! Keep exploring, and who knows what wonders you might uncover next!
FAQ
Understanding these differences is like choosing the right tool for the job. Imagine you’re a detective solving a case – you wouldn’t use a magnifying glass to analyze fingerprints when you have a high-tech forensic kit at your disposal. Similarly, knowing the distinctions helps scientists select the best microscope for their specific needs, leading to more accurate and groundbreaking discoveries.
Specimens are illuminated in light microscopes using visible light, but they do have their constraints. Think of it like taking a photo in low light – things might get a bit blurry. Light microscopes face similar resolution challenges, and they struggle with thicker specimens. It’s like trying to see through a dense fog – not always crystal clear.
Electron microscopes take it up a notch by using electron beams instead of visible light. There are two main types – Transmission Electron Microscopes (TEM) and Scanning Electron Microscopes (SEM). TEMs give us a sneak peek inside cells and tiny structures, while SEMs provide detailed 3D images of surfaces. It’s like having a microscope with different lenses for various purposes.
Absolutely! Light microscopes are like the jack-of-all-trades, used in biology classrooms to study cells or in material science labs to analyze structures. On the other hand, electron microscopes have been instrumental in everything from understanding virus structures to examining nanomaterials. They’re like the superheroes of the microscopic world, revealing details that were once hidden.
Picture this: scientists are detectives, exploring the mysteries of life. Light and electron microscopes are their Sherlock Holmes magnifying glass and high-tech forensic tools, respectively. By choosing the right microscope, scientists uncover secrets, make groundbreaking discoveries, and push the boundaries of what we know about the world around us.
Conclusion:
Now, why does this matter? Well, picking the right microscope is akin to selecting the perfect tool for a job. Imagine using a sledgehammer to hang a picture—it might work, but it’s overkill. Similarly, understanding the strengths of electron and light microscopes allows scientists to tailor their approach based on the scale and detail required for their research.
In scientific exploration, precision is key, and having the right microscope in your arsenal ensures you don’t miss the finer nuances of the microscopic world. Whether you’re diving into the intricate structures of cells or exploring the topography of materials at the nanoscale, choosing the appropriate microscope can make all the difference.
So, in the grand tapestry of scientific discovery, the significance of selecting the right microscope is undeniable. It’s not just about seeing things; it’s about seeing them with the clarity and precision needed to unravel the mysteries that lie hidden. As we navigate the ever-expanding landscape of knowledge, let’s remember that each microscope has its role to play, contributing to the collective mosaic of human understanding. So, scientists, choose your lenses wisely, and let the microscopic revelations continue!
Related Guide
Why do Electron Microscopes have Higher Resolving Power than Light Microscopes?
Why Do Scientists Use Microscopes?
Amazon and the Amazon logo are trademarks of Amazon.com, Inc, or its affiliates.
Leave a Reply